Recomendado por Facundo Olano en su post. https://olano.dev/blog/unit-testing-principles/
Ver libro online, hosteado en Cloudflare R2. Hypothesis link para ver las anotaciones aquí
¿Qué es Branch Coverage? A:¿Cuánto cubre el test? De los If-Else-Switch-Statements o todos los Conditions Like en todos esos caminos.
Q: ¿Cuáles son posibles problemas que el Branch Coverage no puede cubrir? A: No puedes garantizar que el test verifique todos los posibles resultados del programa. Tampoco puede cubrir el comportamiento de librerías externas.
Q:¿Por qué no puedes garantizar que se verifique en todos los casos posibles con la métrica o sea con el testing? A: porque explícitamente tienes que verificar cuál es el input y cuál es el output del test para poder verificar si realmente es lo que esperas.
Q, dos puntos. ¿Por qué no puedes cubrir el compartimiento de librerías externas con testing? Enter. Ah, dos puntos. Ya que no conoces la implementación under the hood de las librerías. Por ejemplo, el método parse de .NET o de Java tienen ciertas branches que no se ven de manera externa en el módulo, por lo que no tienen ninguna forma realmente de testear el resultado.
¿Qué es lo que hace una buena suite de test? Según el autor. Está integrado en el development CI-CD. Solamente se enfoca en las partes más importantes del sistema y otorga el máximo valor con la mínima cantidad de mantención técnica.
¿En qué parte del sistema debería enfocarse de Runic Testing? A, dos puntos. En las partes más críticas del sistema. Aquella que contiene la lógica de negocios por el domain model.
¿Cuál es la definición de unit test según el libro? A, dos puntos. Un unit test es It verifies a small piece of code. Does it quickly. And does it in an isolated manner.
¿Qué es un test double a dos puntos? Es un objeto que reemplaza una dependencia real en un test. Básicamente es una especie de moco, puede ser un stuff también.
¿Por qué un test double? Para realmente testear algo en aislamiento, si una clase tiene una dependencia de otra o múltiples, es necesario reemplazar estas con test doubles.
¿Que es una shared dependency? Es una dependencia que se comparte en distintos tests. Un cambio en esa dependencia afecta a las demás.
¿Que es una private dependency? Es una dependencia que no se comparte entre tests.
¿Que es una out-of-process dependency? Es una dependencia que corre out-of-process; que no esta en memoria. Por ejemplo Levantar un docker con una DB antes de correr los tests.
Differences between Classical and London schools of unit testing
Q: ¿Cuál es la diferencia fundamental entre The London School y The Classical School? A: El componente de isolation/aislamiento en los tests.
Q: Overall, the disagreement between the schools spans three major topics:
- The ---- requirement
- What constitutes a piece of code under test (a unit)
- Handling dependencies A: Isolation
Q: Rellena la tabla con las diferencias entre London School y Classical School
 A:
A: 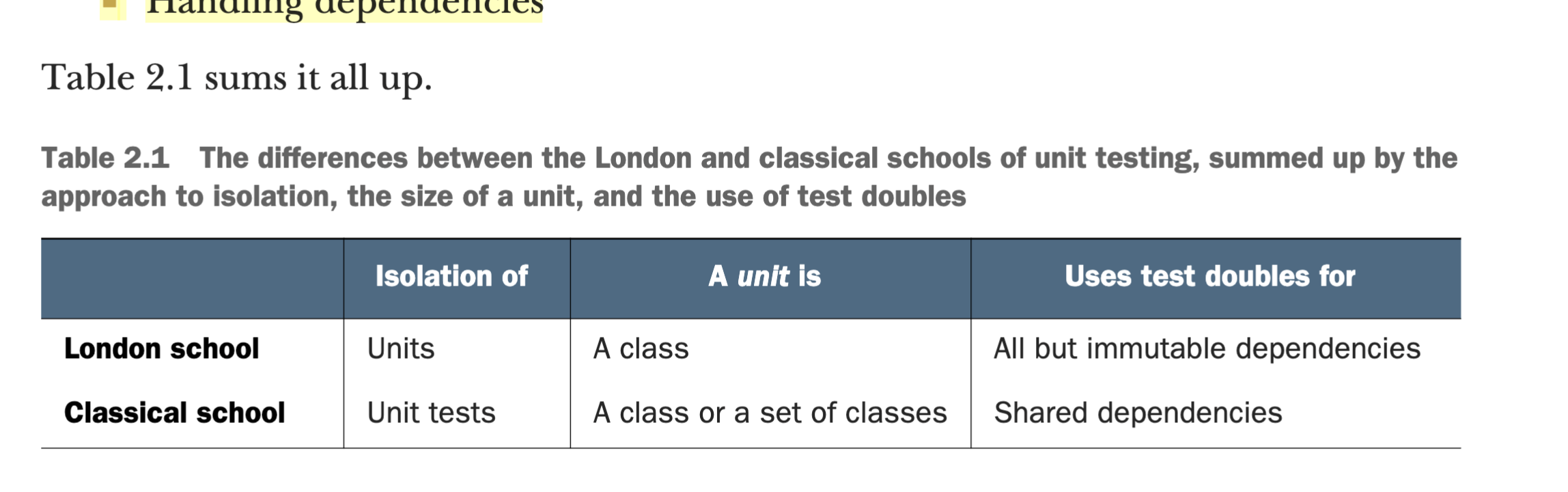
Q: Que school of thought prefiere el autor del libro: The London School or The Classical School? A: The Classical School
Q: Por que el autor tiene de preferencia una School (The London School o The Classical School) sobre el otro? A: The reason is fragility. Tests that use mocks then to be more fragile.
Q: Según el libro, que es units of behavior? A: something that is meaningful for the problem domain, or a business person
Q: Que deberian verificar los tests?
A: Tests shouldn’t verify units of code. Rather, they should verify units of
behavior.
Q: Cuantas clases deberían usar los tests? A: No importa la cantidad de clases. El objetivo es que verifiques una Unit of Behaviour.
Q: ¿Cual es la analogia de contar una historia con un test? A: Un test deberia contar una historia sobre un problema que tu código ayuda a resolver, y esta historia debería tener sentido e importancia para una business person.
Notes del video
What is a structural inspection? It’s when you test the implementation details.

Why is this test a bad example of testing? Because it’s testing the structural part of the code.
What is a test should focus? A good test should bind to the end result, not implementation details.
The idea of a test is to verify the end result, not implementation details.kkA
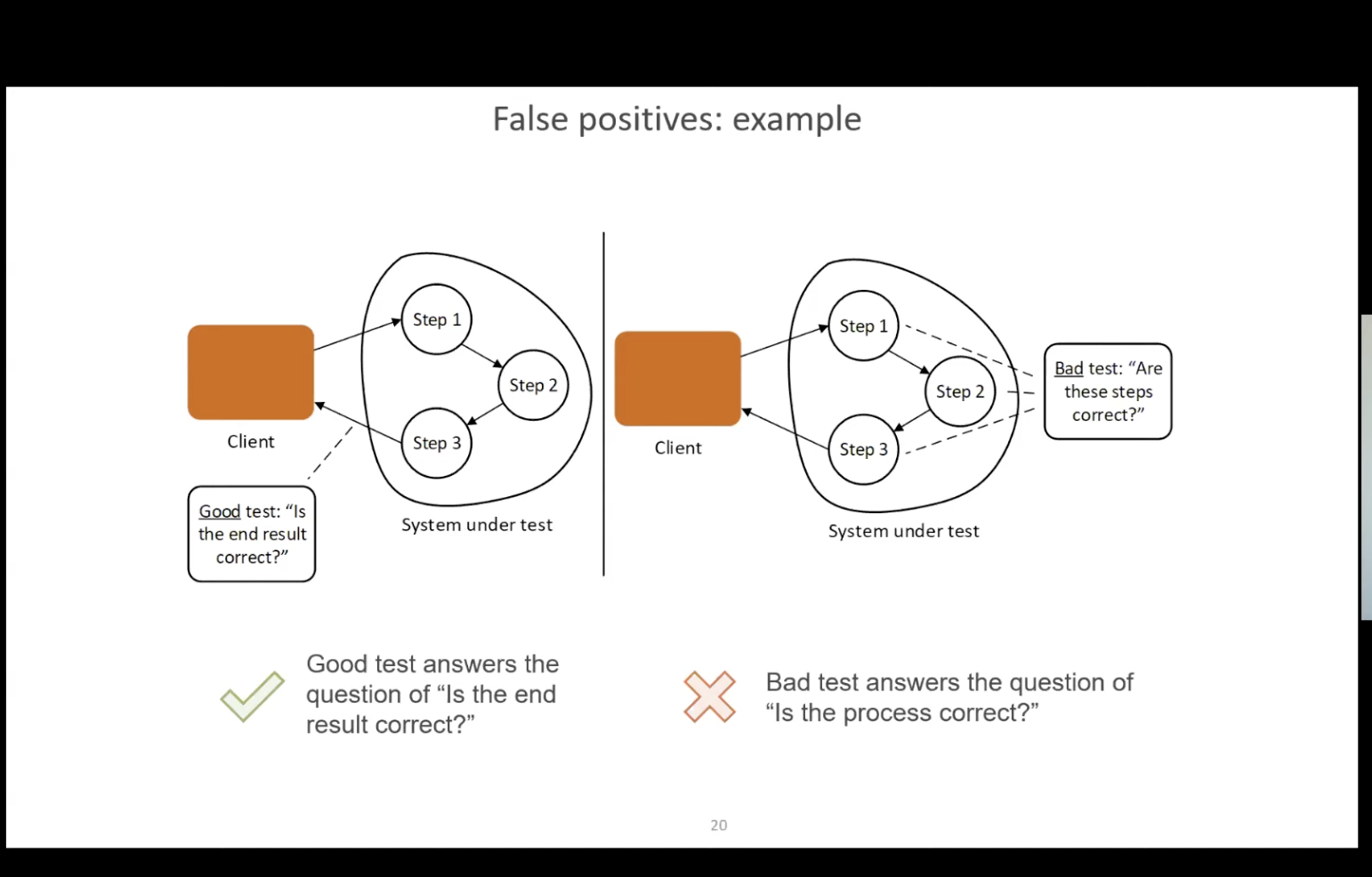 t. 16:20
t. 16:20
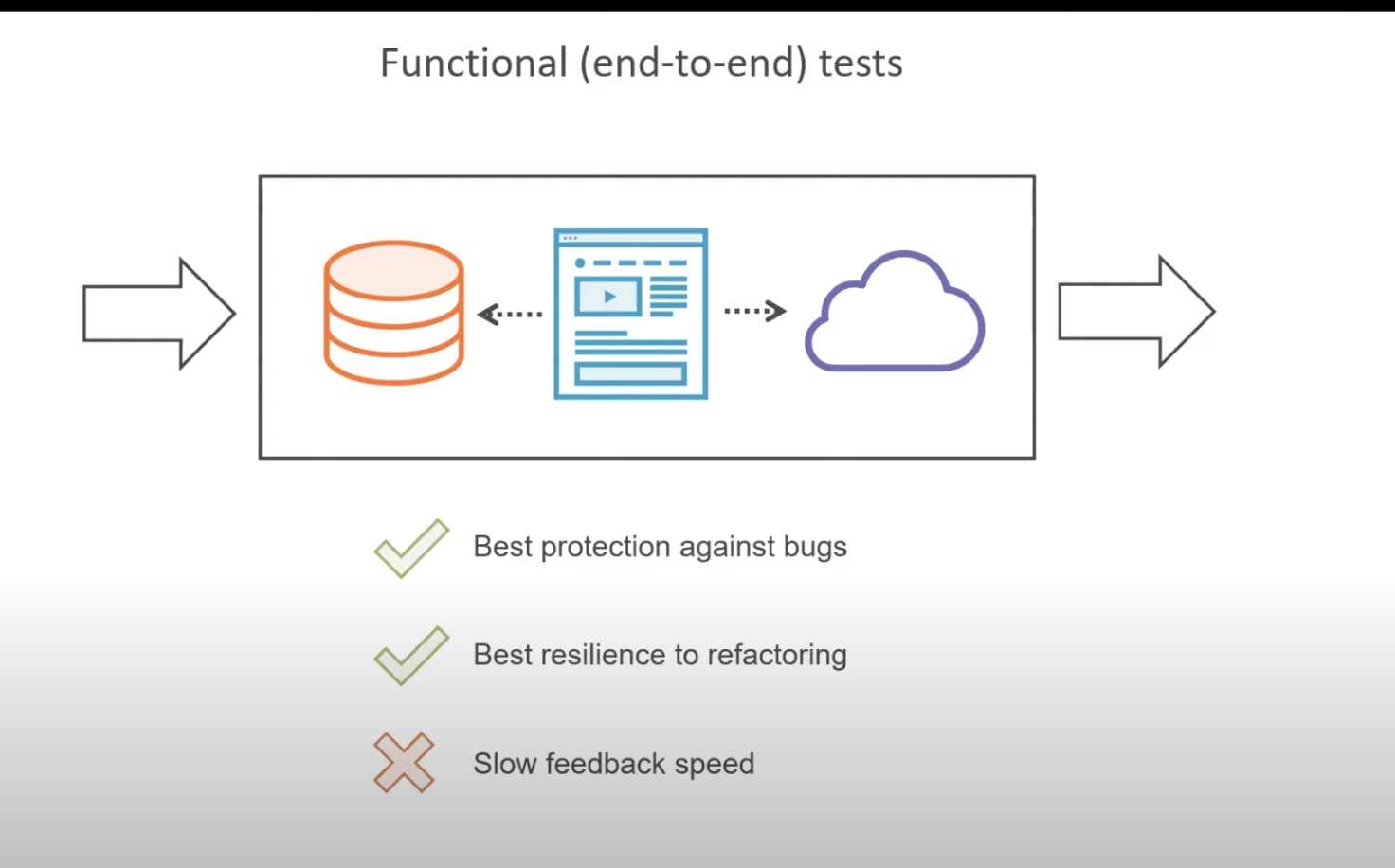 t.23:55
t.23:55
 t. https://youtu.be/k_ItB5btREU?t=1482
t. https://youtu.be/k_ItB5btREU?t=1482
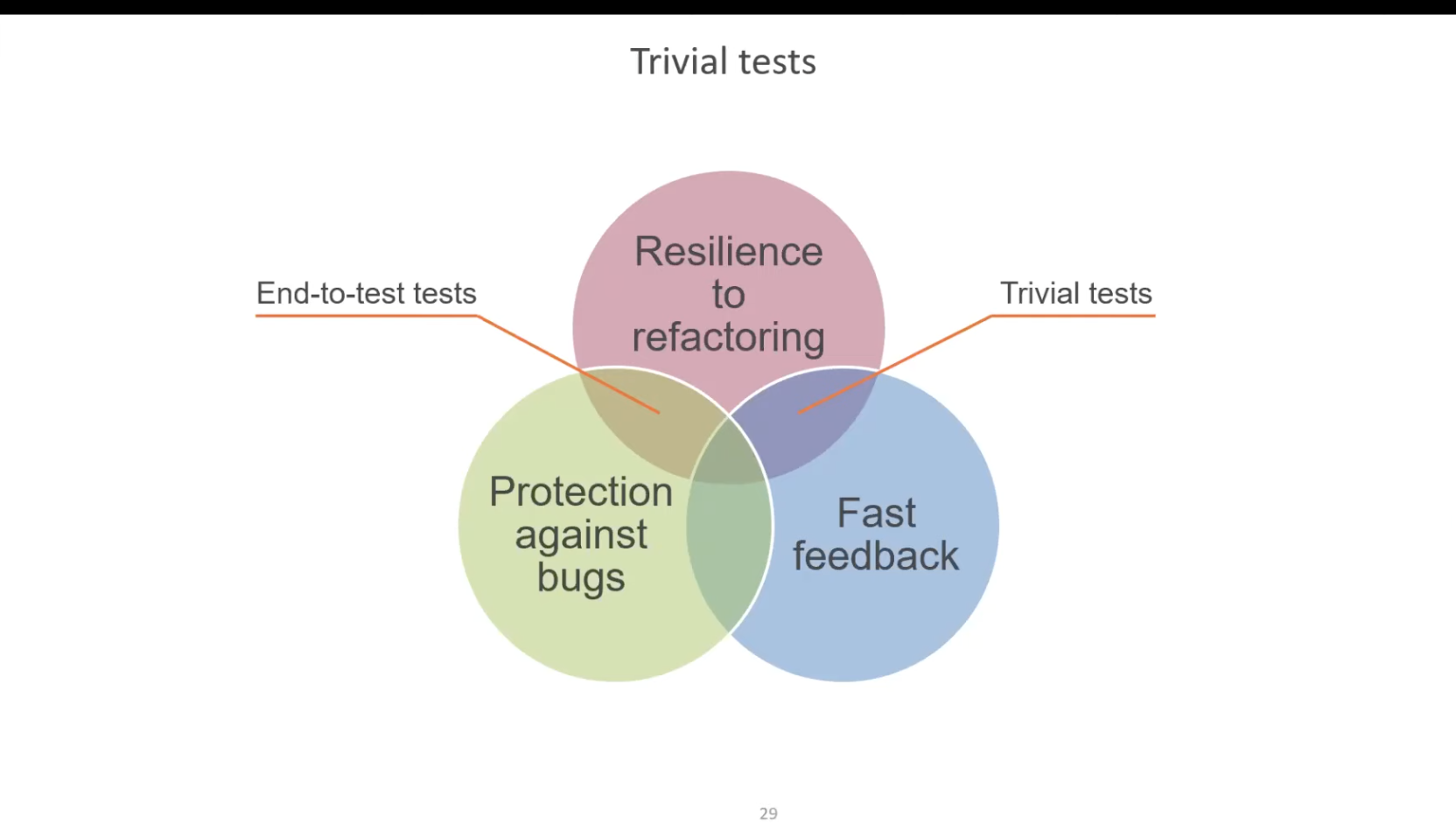

Effective unit test is tightly coupled to production code.
 https://youtu.be/k_ItB5btREU?t=1945
https://youtu.be/k_ItB5btREU?t=1945
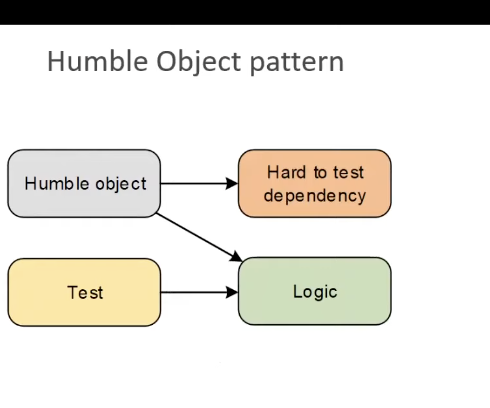 pregunta ¿Qué es un Humble Object Pattern? Un Humble Object Pattern es una forma es un patrón que separa el código un poco difícil de testear a una clase distinta separada en otro módulo separada en otro módulo
pregunta ¿Qué es un Humble Object Pattern? Un Humble Object Pattern es una forma es un patrón que separa el código un poco difícil de testear a una clase distinta separada en otro módulo separada en otro módulo
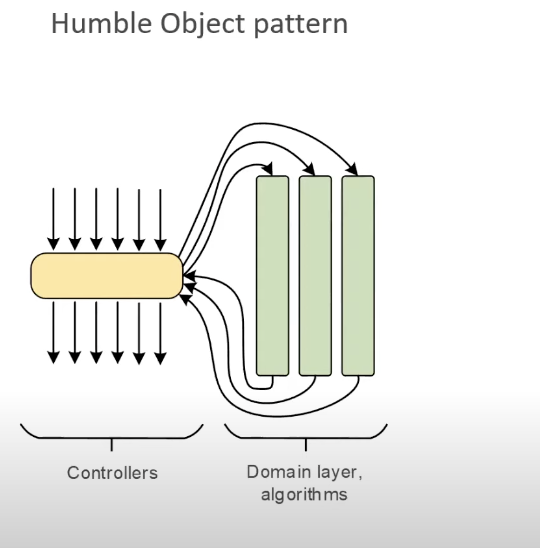
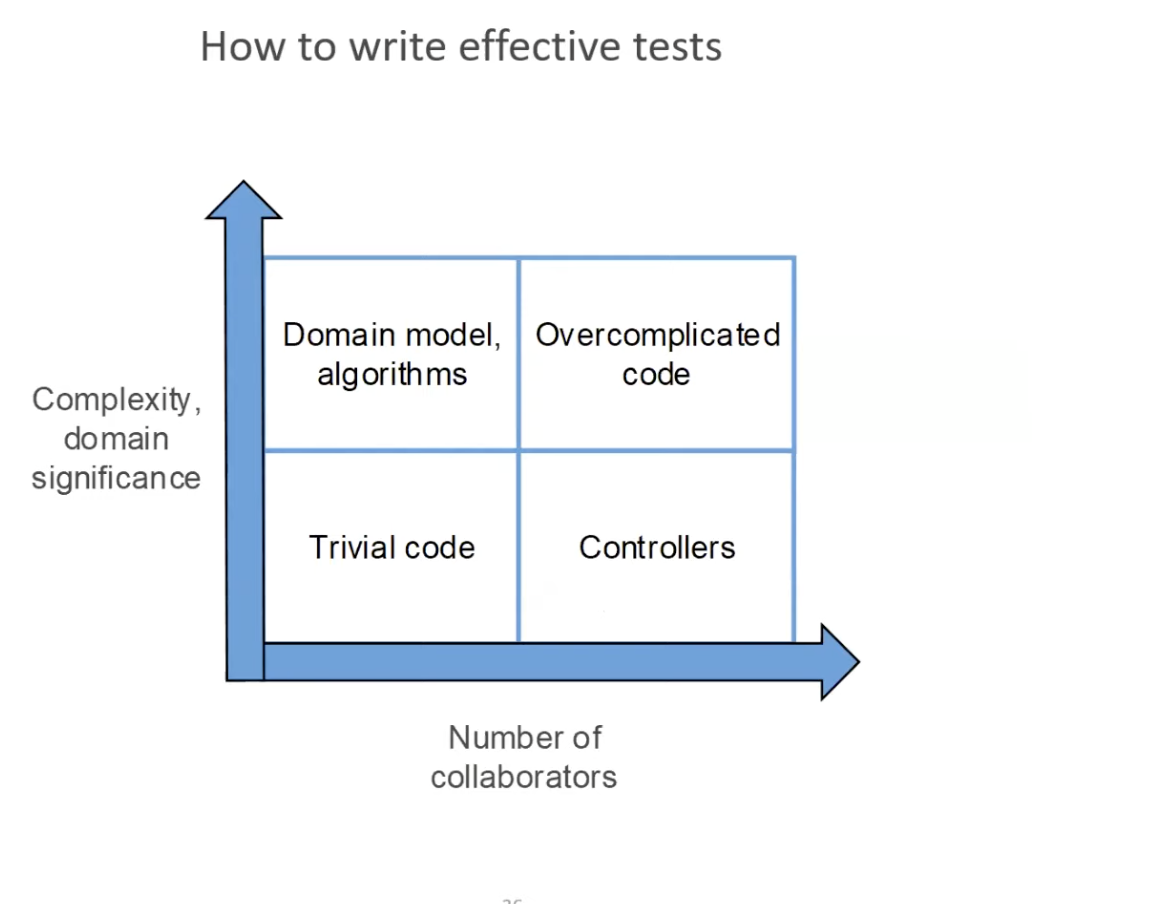
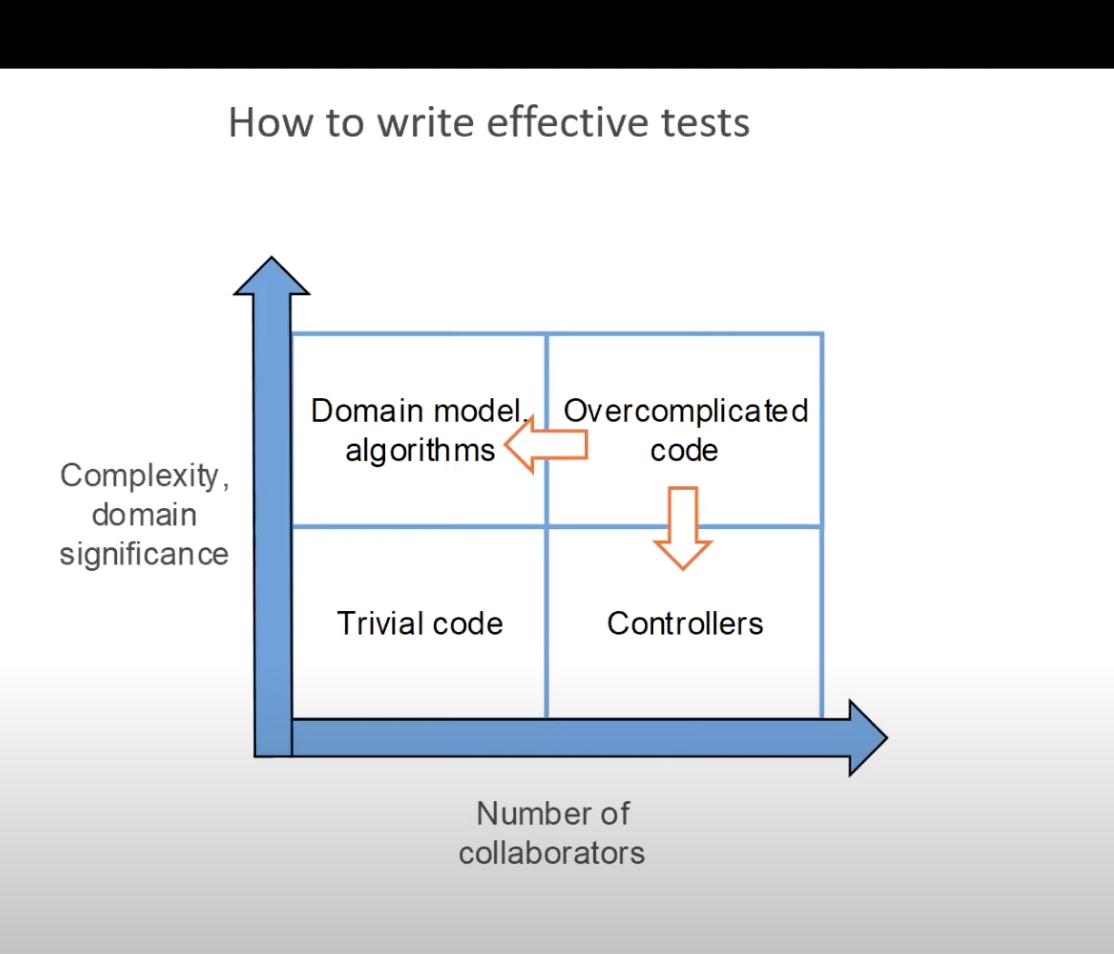
When you have overcomplicated code, you should split it into controller or domain model algorithms.
Cuando tienes partes en el código que son difíciles de testear, trata de mover lo más posible de la lógica a un módulo aparte, para así poder testear más fácilmente.
En programación, ¿cuál es un ejemplo de implementación de Humble Object Pattern? En frameworks como Ruby on Rails o .NET. Model View Controller. El Model se encarga de la lógica, View es el Hard to Test Dependency y el Controller es el Humble Object.
When to mock
¿Qué es un móc?
Why use mocks To remove external dependencies when testing.
Me falta entender acá
In testing, the objective of mocks is to maintain backwards compatibility.
What type of dependencies should be replaced by Mocks? Only unmanaged dependencies should be replaced by mocks.
Why using AI is a bad option to write tests? Because AI doesn’t understand the business logic the way a human does. It can’t reliably differentiate what is important for the business and what is not.
In testing, it doesn’t matter. To test the code per se, what matters is testing units of behavior. The observable part of the code is what matters.
Chapter 3
Q: Q: Cómo deberias nombrar tus tests? A: Como si le estuvieras describiendo un escenario a un no-programador, o alguien que no es familiar con la programación.
Q: Why using the wording ‘should be’ is an anti-pattern? A: Because a test is a single, atomic fact about a unit of behaviour. There’s no place for a wish (should be) when deciding a fact
Q: Is this a good or bad name for a test?public void Delivery_with_past_date_should_be_invalid() A: bad test. Because a test is a fact. It’s not a wish.
Chapter 4
Q: What problem can cause bad implemented tests? A: Los developers no confian en ellos.
Q: Que pasa cuando un test esta muy acoplado con los implementation details? A: Genera falsos positivos.
Q: When a test is coupled to its implementation details, every refactor makes the test ----? A: fail
Q: Tests that couple to the SUT’s implementation details ----- to refactoring A: are not resistant
Q: Que es SUT? A: System under Test.
Q: Cual es una analogia para estructurar un test según el libro? A: Como si estuvieras contando una historia.
Q: What should you aim when creating a test? A: To the end result.
Q: What are ways to avoid brittleness in tests? A: By not focusing on implementation details of the code. Just the final result.
Q: What this diagram represents:
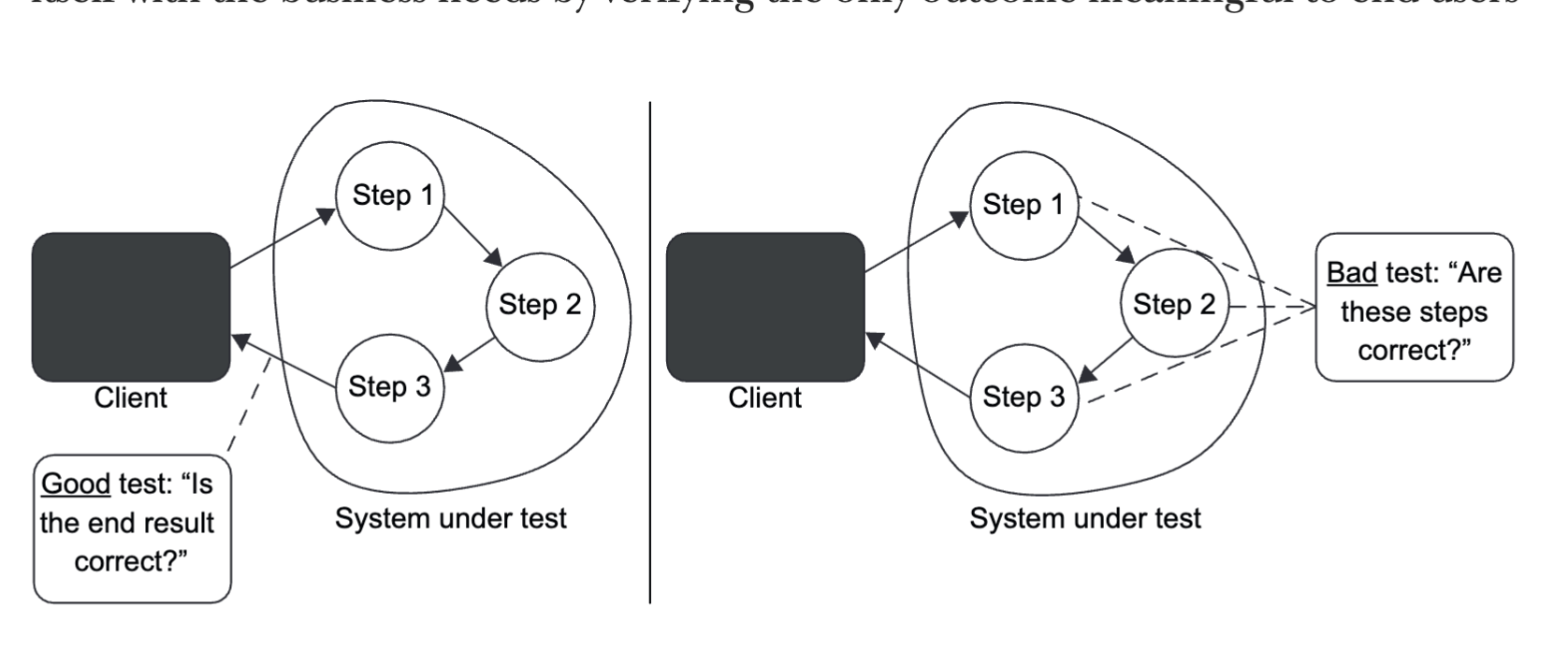 A: The diagram on the left represents when a SUT is observing the observable behaviour. The diagram on the RIGHT is tied to implementations details.
A: The diagram on the left represents when a SUT is observing the observable behaviour. The diagram on the RIGHT is tied to implementations details.
Q: Rellena la informacion faltante: 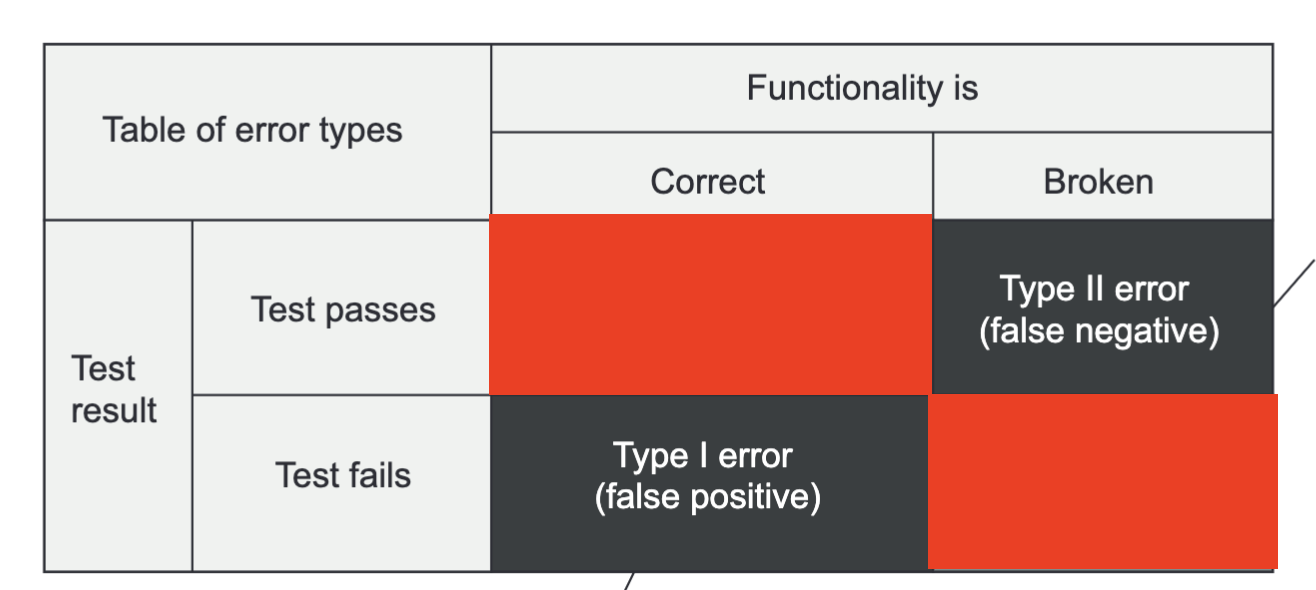 A:
A: 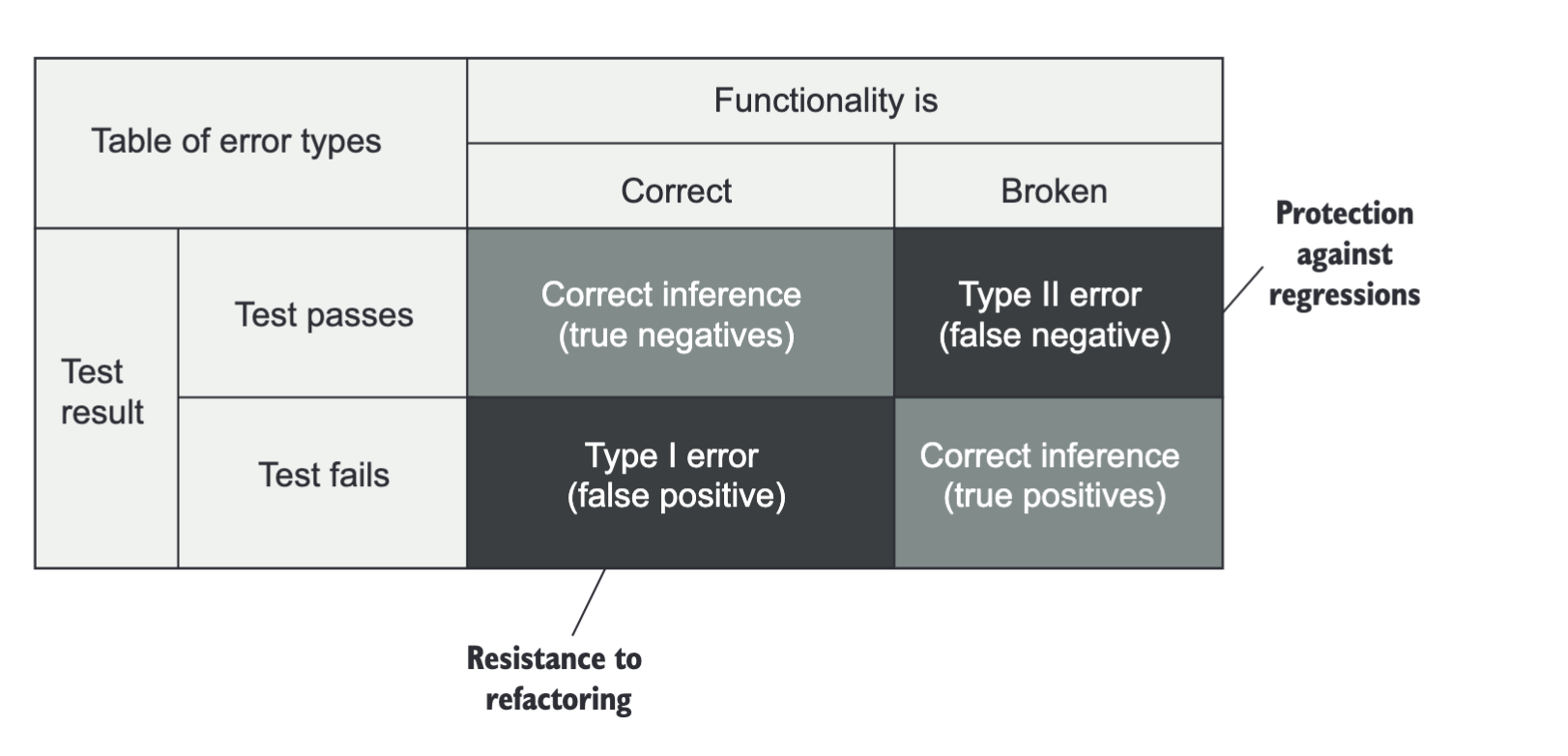
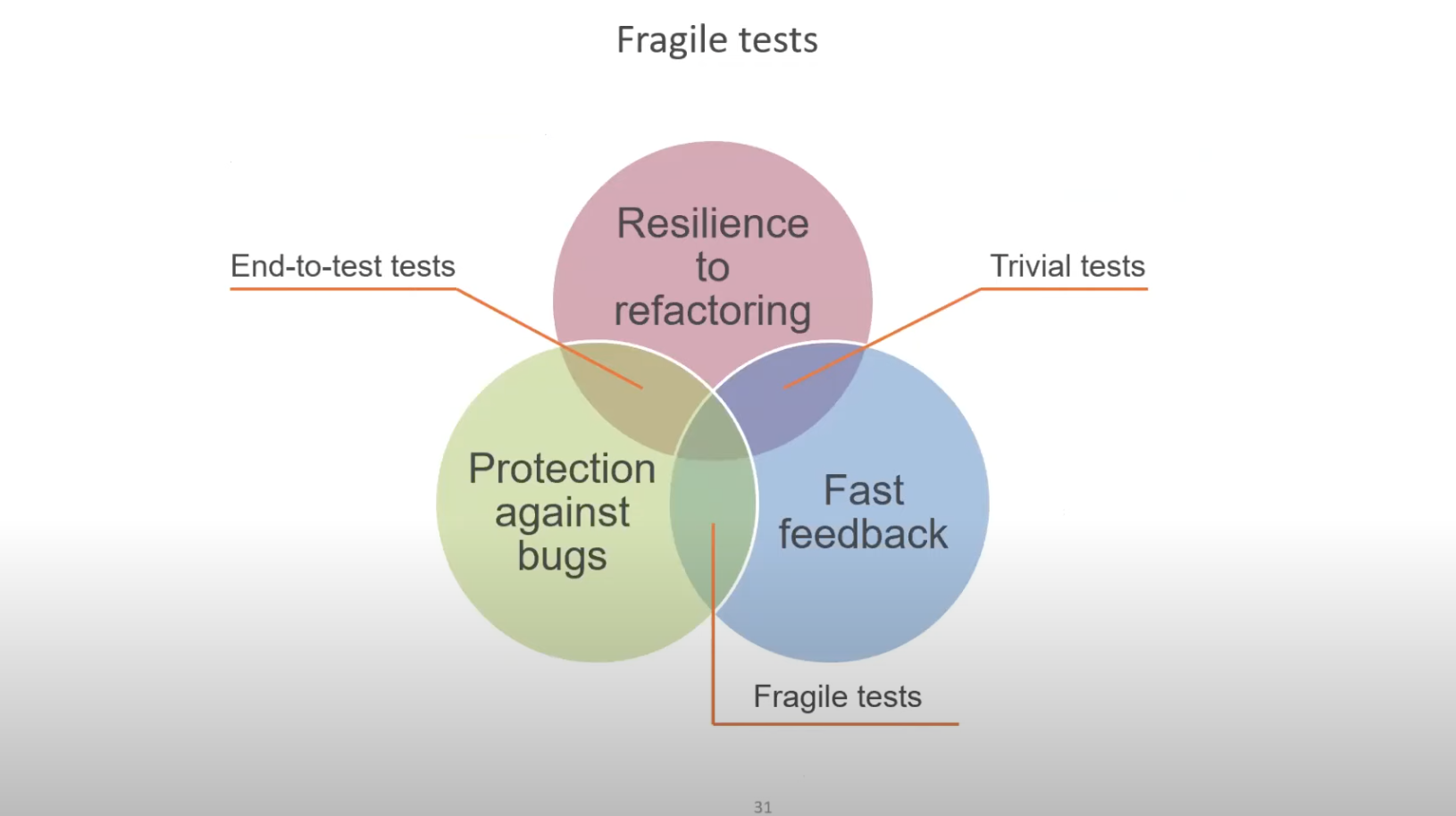
Q: Rellena el diagrama de protection agsint regressions and resistance to refactoring
A: 
Q: A test is more accurate when one of the following is predominant: (signal: number of bugs found, noise: number of false alarms raised) A: when it generates a strong signal of numbers bugs found.